An Introduction to Entity/Relationship Profiling
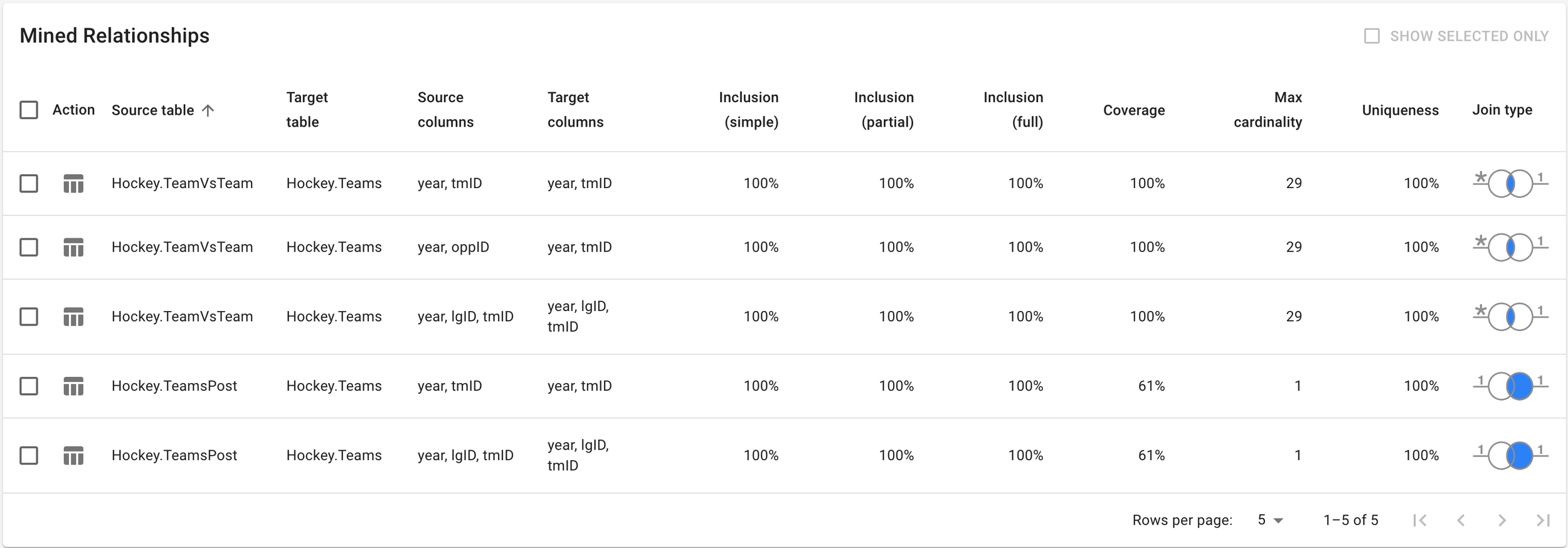
Mined Relationships table in DataViadotto Profiler
Entity/Relationship modelling aims at a conceptual model of data that describes the entities and relationships for a domain of interest. For example, an organisation may want to describe what data they need for their customers or products, and - likewise - for sales and acquisitions. Customers and products represent two types of entities, and sales represents a type of relationship between customers and products. An E/R model is an information structure that can be implemented as a database. It represents the things that a business needs to operate. Hence, the business requirements determine the ER model, which in turn determines the data that will be managed by the database derived from the ER model. Simply put, the model determines which data will need to be managed.
In the era of data, however, organisations have no choice but assess for any given data asset how relevant it may be to their business functions, internal or external. If the data is relevant, the asset needs to be integrated and the existing models of data evolve. In other words, data impacts the model. More so, companies aim to service their customers with insight stories that are assembled from data about the business entities and relationships that are of interest. In a database, business entities can be uniquely identified by keys, and relationships are implemented in the form of foreign keys. In fact, keys ensure entity integrity and foreign keys ensure referential integrity. As such, keys and foreign keys are cornerstones of databases, fundamental to update and query operations. Only a data model that is perfectly aligned with its data can ensure high data quality. And only high quality data can enable high quality analytics, machine learning, prediction and business value.
We have therefore proposed the concept of E/R Profiling as the discovery-oriented, data-driven counterpart to E/R Modelling. More specifically, E/R Profiling is the task of finding all ways in which business entities and relationships can be identified uniquely from a given repository of data sets. This is done in multiple steps: 1) Discovering all keys and uniqueness constraints that hold on a given data set, 2) discovering all foreign keys and inclusion dependencies that hold on all pairs of given data sets, and 3) identifying all those keys, uniqueness constraints, foreign keys and inclusion dependencies that are sensible for the domain of interest. Task 3 cannot be fully automated and requires domain expertise. Methods for E/R Profiling need to work on large data sets that may suffer from data quality problems, including duplicate, missing, or inconsistent data.
While plenty of fantastic algorithms and prototypes on (approximate) constraint mining have been brought forward in academia, no tools have been available that start to address E/R Profiling as a whole. Commercially available tools are expensive since they are part of sophisticated data governance/quality systems, and have very limited capabilities, such as restricting key/foreign key discovery to key/foreign key analysis where the validity of a given key or foreign key is simply calculated.
We are pleased to say that DataViadotto is now offering the first E/R Profiler.